SmartFactory training line
SmartFactory = demonstration of the latest technologies and principles of Industry 4.0
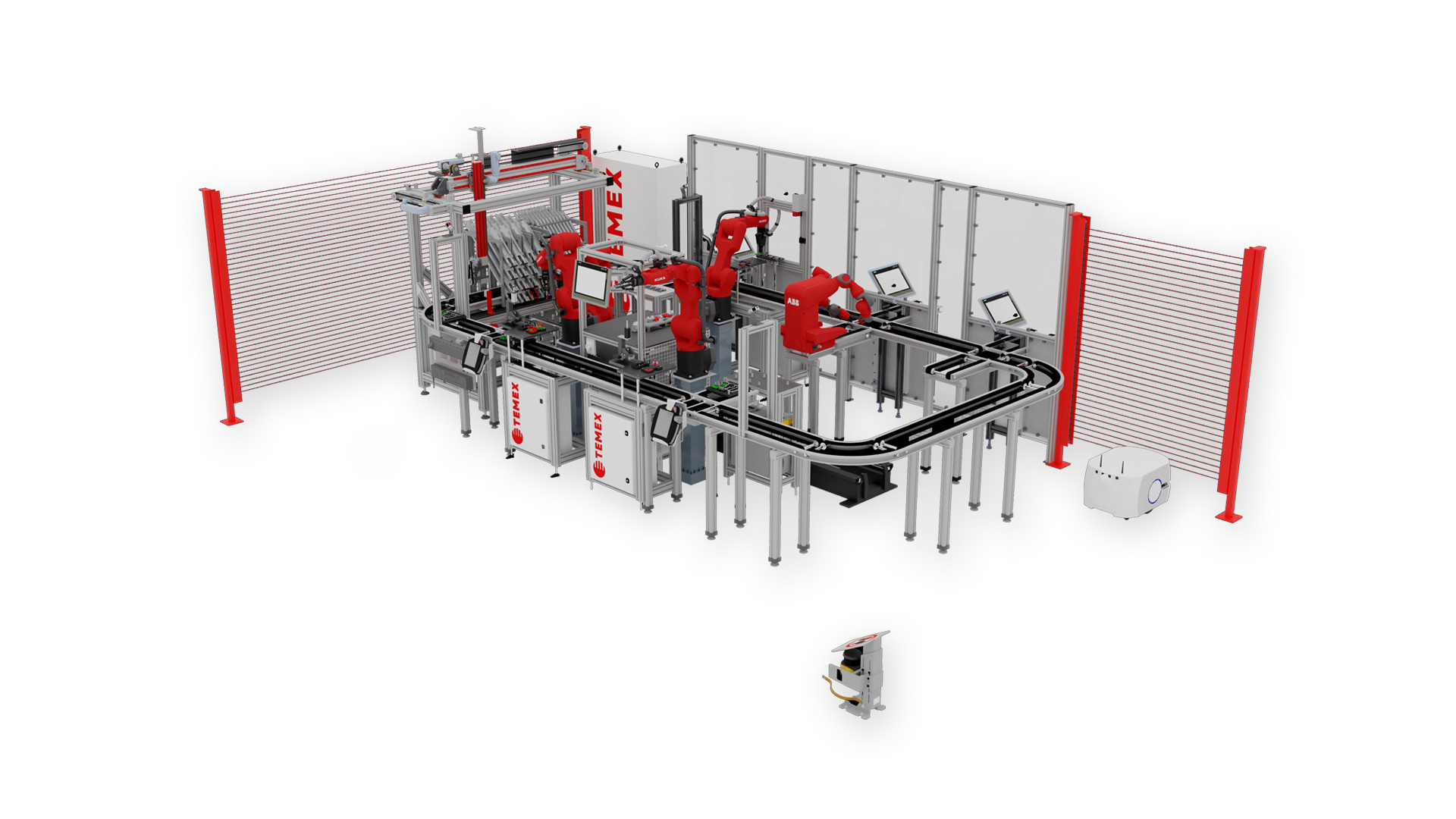
SMARTFACTORY – ASSEMBLY LINE INSTRUCTION FOR THE AUTOMATED AND MANUAL ASSEMBLY OF PRODUCTS
Name of contract: SmartFactory – Testbed Industry 4.0 CPIT TL3
Delivery term: In progress
SPECIFICATION
The complete delivery, including design, implementation, integration and delivery of the production environment for assembling products made from Lego parts, Lego building base and electronic components. At the end of its production cycle, an inspection will be performed for each product at a test station, including generating and recording an output report on the correctness and functionality of the product.
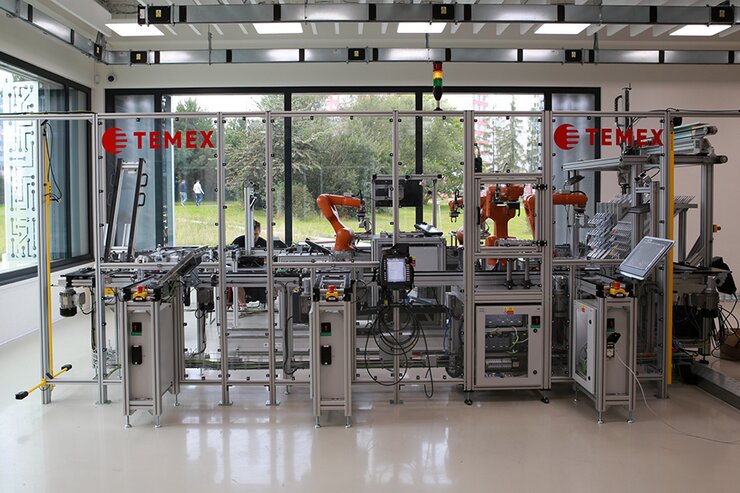
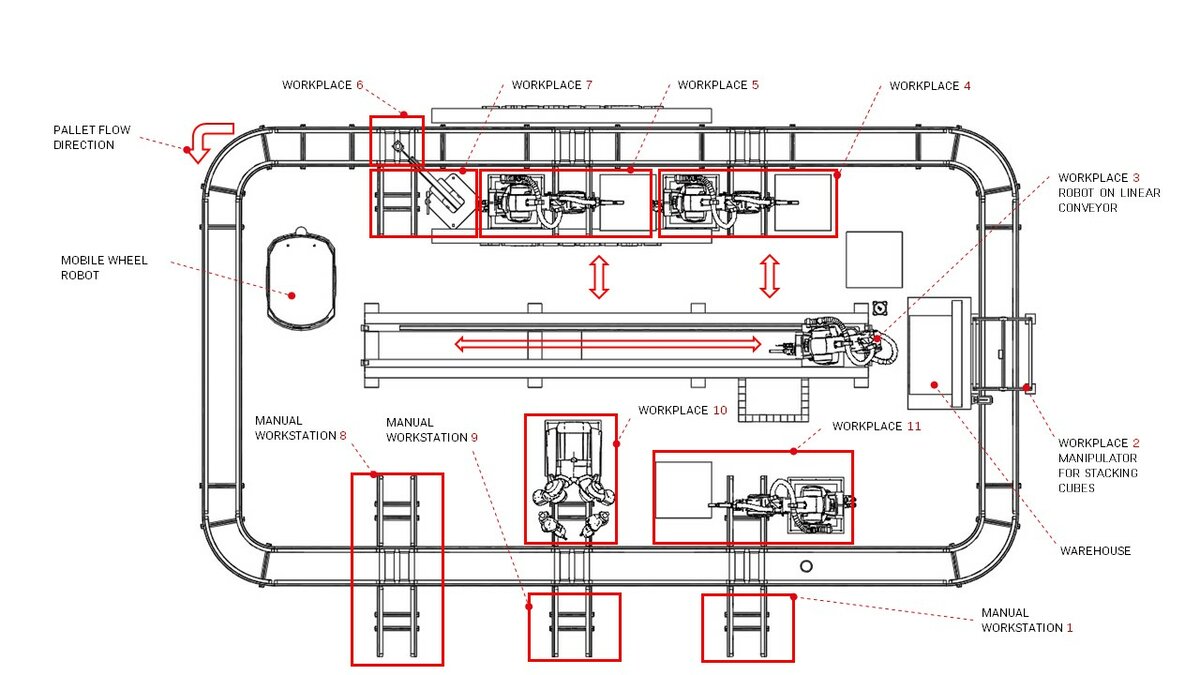
LAYOUT OF THE LINE
BASIC CHARACTERISTICS
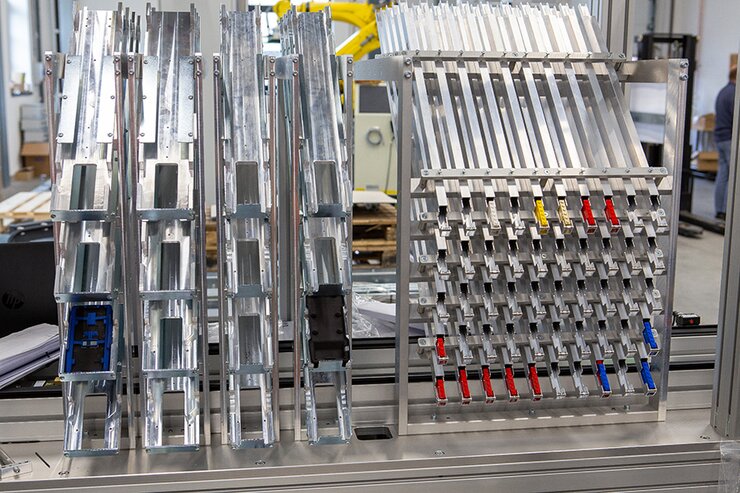
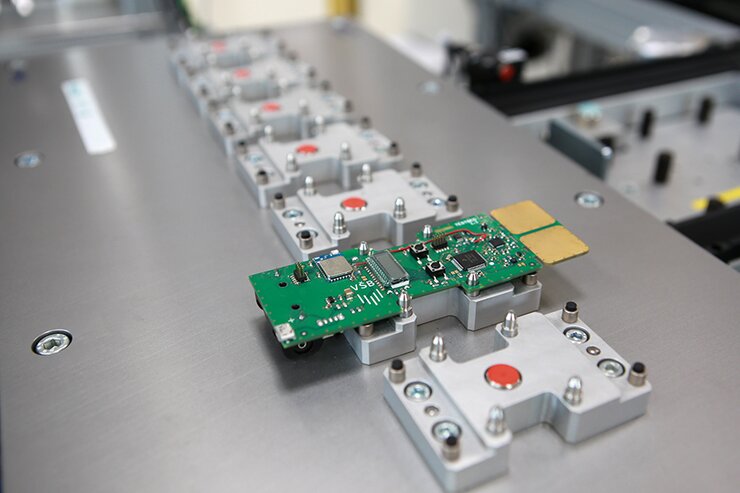
The product of the line is composed of a Lego part. In addition, each product will contain an electronic circuit that gives the product a specific function. The individual building components will be placed on the Lego building base and after assembly they will form a compact unit. The SmartFactory line is designed for the assembly of three types of products with the possibility of the subsequent expansion of the product base.
KEY FUNCTIONS OF THE LINE
- The production system carries out both the automated and manual assembly of products.
- The product consists of Lego building blocks, blocks created with a 3D printer and electronic components.
- The configuration of the product and production method are selected at the beginning of the production cycle using a graphical user interface on the operator panel and on a mobile tablet device (“product configuration”).
- At the beginning of the assembly cycle of a new product, an empty product container is taken from stock and prepared.
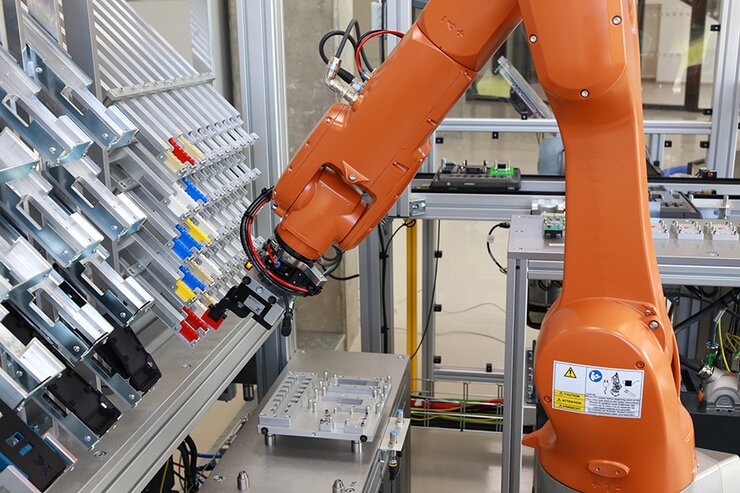
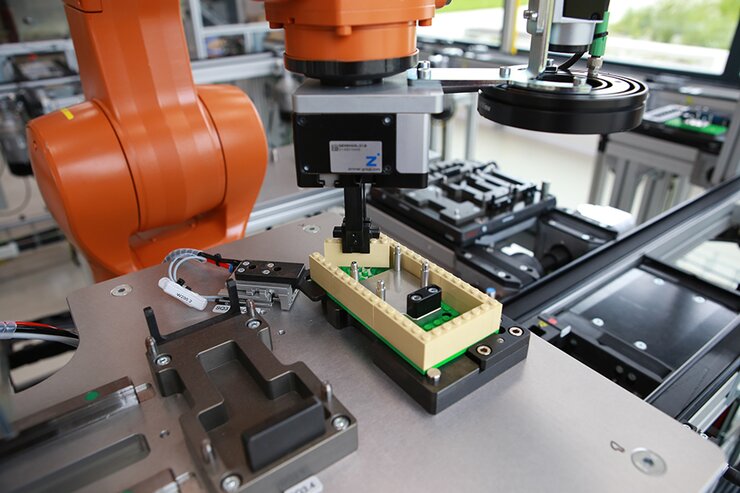
- Based on the configuration of the product, the manipulator takes all parts of the selected product, including the electronic circuit, from stock and loads them into the product container.
- A check is made that the container contains all the required parts (each part is marked with a QR identification code) and the prepared set/container is placed on the platform of the conveyor system.
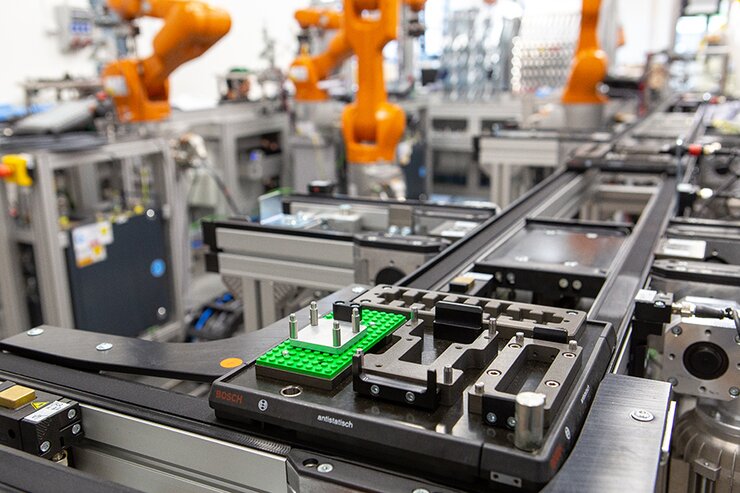
- Each Lego base will contain a memory identifier (RFID), which will contain all the information about the individual parts of the product and all the operations that are to be carried out on it.
- The control system verifies which of the workplaces has free production capacity and assigns the processing of the order to this workplace, i.e. transports the product container with parts to it and launches the operation.
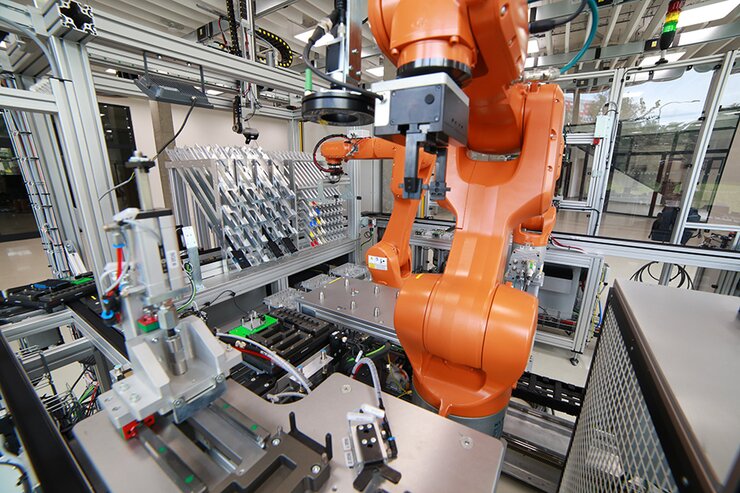
- The assembly process will be based on machine vision and the guidance of the robot by camera.
- The robotic cells will be able to produce “their” defined product independently of each other.
- Complete warehouse management will be implemented by MES (Manufacturing Execution System).
- If manual assembly is selected in the initial configuration, the containers with the prepared product parts will be transported to the selected manual assembly workplace, where the assembly will be performed by the operator.
The aim of the line is:
- Interoperability – The ability of cyber-physical systems to communicate with each other through information systems.
- Virtualization – A virtual copy of SmartFactory connecting data from sensors with the virtual and simulation models of the factory.
- Decentralization – The ability of the cyber-physical system to act autonomously within SmartFactory.
- Working in real time – The ability to analyze the data obtained in real time and intervene in the production process in real time.
- Service orientation – Cyber-physical systems offer and provide services for manufactured products or to operators.
- Modularity – The ability to adapt SmartFactory to change.